AI Data Privacy: How Your Information Is Used and Protected
AI Data Privacy: How Your Information Is Used and Protected
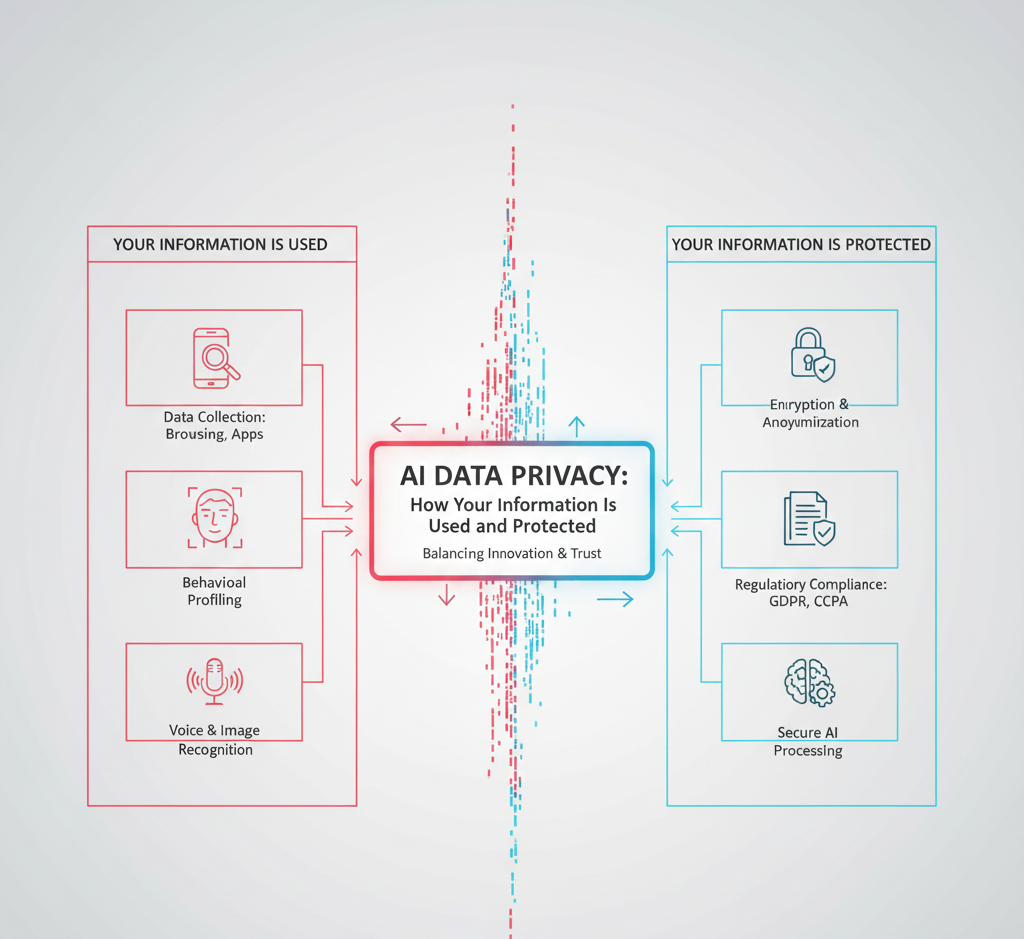
As artificial intelligence is becoming more and more ingrained in the daily lives of people, there is a rising worry regarding the privacy of data. The huge quantities of personal and corporate data that artificial intelligence systems depend on in order to operate properly bring up problems concerning the methods utilized to gather, store, use, and secure information. Individuals, corporations, and legislators must understand data privacy as it pertains to artificial intelligence in order to strike a balance between technological innovation and security and trust.
The Ways in Which Data Is Utilized by Artificial Intelligence
By examining data, artificial intelligence systems are able to identify patterns, formulate predictions, and provide outputs that are customized to meet the requirements of certain activities. Browsing history, purchasing behavior, location information, health records, or even user-generated material such as emails, messages, and social media activity are all examples of the types of data that may be included. AI is capable of creating individualized suggestions, enhancing consumer experiences, optimizing corporate processes, and improving decision-making by analyzing massive information.
In order to train successfully, machine learning models often need the use of labeled datasets. For instance, an artificial intelligence system that has been developed to identify illnesses using medical pictures acquires its knowledge by examining thousands of scans that have been annotated. In other instances, artificial intelligence systems are able to continually learn from the interactions that users have with them, which leads to an improvement in their predictions and outputs as time goes on. Because of this dynamic data consumption, privacy and security have become crucial factors to take into account.
Dangers that Threaten the Privacy of Information
There are a number of dangers that are presented by the widespread use of personal information in artificial intelligence. Sensitive information might be exposed as a result of data breaches, unlawful access, or incorrect treatment. In addition, there is the possibility that artificial intelligence algorithms might unintentionally preserve patterns from individual data points, which raises worries about the potential for re-identification. Artificial intelligence has the potential to make judgments that disproportionately affect certain groups of people depending on the data that has been processed by the system. As a result, bias and abuse of data are two serious concerns.
Methods and strategies to secure information
In order to reduce the dangers that come with breaches of privacy, artificial intelligence engineers make use of a number of different approaches. Prior to being processed, data anonymization eliminates any information that might be used to identify someone, hence decreasing the likelihood that data can be traced back to specific persons. Data is safeguarded by encryption while it is being transported as well as while it is at rest, preventing unauthorized entities from gaining access to it. Federated learning is a novel method of training artificial intelligence models across a variety of devices without consolidating raw data in a single location. This allows for the preservation of personal information on local devices while simultaneously enhancing the overall performance of the models.
Compliance and Regulatory Frameworks
In order to safeguard individuals’ private information in artificial intelligence (AI) applications, governments and regulatory organizations have created legislation. The way in which corporations are required to acquire, retain, and use data is determined by regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. Ensuring that these standards are followed guarantees openness, offers users the ability to exercise control over their own data, and establishes sanctions for any abuse or breaches of their data.
Openness and Control by the User
Transparency about the collection and use of data is a need for the responsible utilization of artificial intelligence. It is becoming more and more common for companies to make available privacy policies, permission forms, and methods for consumers to control or remove their data. Providing consumers with the ability to manage their own data not only helps to establish trust, but it also adheres to the principles of ethical artificial intelligence.
Implementation of Artificial Intelligence Security Protocols
Artificial intelligence systems must be able to withstand assaults in addition to protecting privacy. There are two types of assaults that are of great concern: adversarial attacks, in which harmful inputs are used to try to affect the outputs of artificial intelligence, and model inversion attacks, which seek to extract data from trained models. In order to safeguard both artificial intelligence systems and data from being exploited, it is critical to have strong security protocols, continuous monitoring, and periodic audits.
Finding the Right Balance between Innovation and Privacy
Artificial intelligence innovation is dependent on data, but it is important to keep privacy regulations in mind. Techniques such as the development of synthetic data, privacy-preserving machine learning, and stringent compliance frameworks assist in achieving a balance between the advantages of artificial intelligence and the need for security. By making data privacy a priority, companies may increase user trust, boost adoption rates, and decrease the likelihood of legal and ethical issues.
Data Privacy in the Age of Artificial Intelligence
As artificial intelligence continues to develop, so too will the concept of data privacy. Increased usage of edge computing, which is characterized by data processing that takes place on local devices, and artificial intelligence systems that are able to make predictions without accessing raw personal data are among the emerging trends. In the age of artificial intelligence, ethical frameworks, stricter legislation, and technical advancements will continue to be crucial in protecting individuals’ personal information.
When it comes to artificial intelligence, data privacy is an essential consideration that influences the methods by which individuals’ information is gathered, analyzed, and safeguarded. In order to ensure the continued maintenance of trust, security, and ethical responsibility, enterprises may make use of artificial intelligence while also adhering to legal compliance, implementing technological protections, and maintaining transparent processes.