How AI Trains Itself: Reinforcement Learning Explained Simply
How AI Trains Itself: Reinforcement Learning Explained Simply
The field of reinforcement learning (RL) is one of the most exciting areas of artificial intelligence, since it enables computers to learn by trial and error rather than through explicit instructions. In contrast to conventional programming, which entails humans establishing regulations and results, reinforcement learning enables artificial intelligence systems to investigate their surroundings, come to conclusions, and enhance their performance during the course of time as a function of feedback. Applications like as autonomous cars, recommendation systems, robotics, and gaming are powered by this technique.
A Comprehensive Overview of Reinforcement Learning
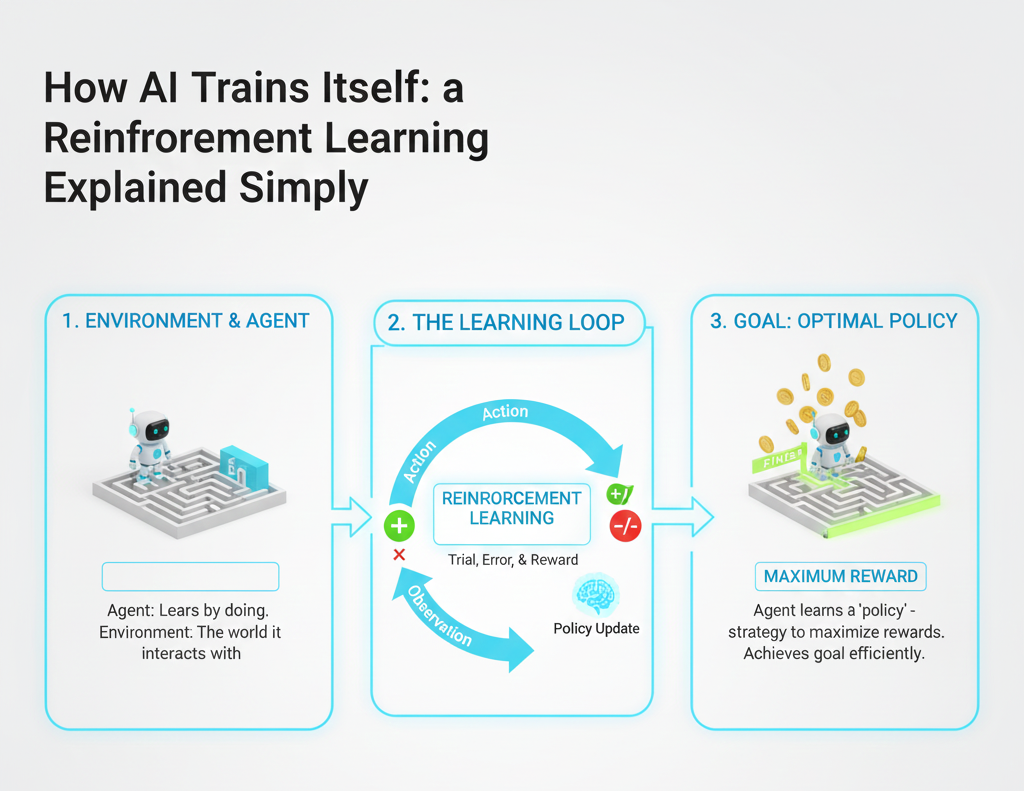
The fundamental purpose of reinforcement learning is to train an artificial intelligence agent to accomplish a certain objective via its interactions with the environment in which it is situated. The agent takes activities, observes the consequences of those actions, and gets feedback in the form of either a reward or a penalty. The agent gains an understanding of which behaviors yield more favorable outcomes as time passes, and it slowly formulates tactics that maximize the total amount of rewards that it receives. The process of trial and error is similar to the way that people and animals learn how to behave in the actual world.
The Most Important Parts of Reinforcement Learning
The agent, the environment, actions, and rewards are the four primary components that make up a reinforcement learning system. The artificial intelligence model that is making choices is referred to as the agent. The agent functions inside its environment, which may be a game, a simulated world, or a real-world situation. The environment can be considered the context in which the agent operates. At every given instant, the agent has a number of different actions it might do, and rewards are offered as feedback to indicate whether or not the action is bringing the agent closer to achieving its objective.
An Explanation of the Mechanisms Behind Learning
The agent’s exploration of the world is done in a random manner, and this marks the beginning of the learning process. Every action that is taken results in either a reward or a punishment, and the agent use these outcomes to refine its approach. Through the course of several iterations, the artificial intelligence is able to recognize patterns and determine which behaviors provide the most favorable results. This method depends on finding a balance between exploration, which involves attempting new activities in order to uncover more effective tactics, and exploitation, which involves using established techniques that are likely to provide significant benefits.
Use in the Fields of Gaming and Simulation
The success that reinforcement learning had in the gaming industry brought it to the forefront. Artificial intelligence agents that have been educated by reinforcement learning have surpassed human champions in the games of chess, Go, and real-time strategy games. These agents acquire intricate tactics by playing hundreds or even millions of simulated games, modifying their strategy in response to wins, losses, and outcomes that occur in between. Before being used in real-world situations, gaming offers a controlled environment in which to perfect reinforcement learning methods.
Robotic Systems and Autonomous Technology
Reinforcement learning, which is used in the field of robotics, allows robots to acquire complicated abilities like as walking, grabbing items, or negotiating terrain that is unexpected. Before being deployed in practical situations, robots undergo training in simulations where they practice learning ideal movement patterns. The use of RL also provides benefits to autonomous cars, since AI systems are able to make real-time driving judgments by simulating a large number of traffic situations and modifying their behavior according to safety and efficiency requirements.
Personalized Experiences and Recommendation Systems
Recommendation engines that are used by social networking platforms, e-commerce websites, and streaming services make use of reinforcement learning (RL). Artificial intelligence agents are able to determine which recommendations will increase the amount of time that users spend on a site, the number of clicks they make, or the number of sales they make. Reinforcement learning enables tailored experiences that improve over time without human rule-setting by constantly modifying suggestions depending on the behavior of the user.
Difficulties Associated with Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning, while it is strong, is faced with problems such as the need for a significant quantity of data, extended training timeframes, and the need for incentive systems to be carefully designed. In the actual world, incentives that are not well designed might result in unexpected actions, therefore it is necessary to take safety, ethics, and unpredictability into consideration while applying them. Reinforcement learning (RL) continues to make tremendous progress in both academia and industry despite these obstacles.
Advancements in the Field of Reinforcement Learning
Hybrid systems that are capable of making more complex decisions will be developed via the growing integration of reinforcement learning with other artificial intelligence methods, such as supervised learning and unsupervised learning. As the capabilities of simulation and computer power continue to improve, reinforcement learning will continue to extend its reach into fields such as healthcare, finance, robotics, autonomous cars, and other areas where adaptive, intelligent behavior is of the utmost importance.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the ability to teach itself via experience, progressively increasing performance without explicit instructions, as shown by reinforcement learning. Through the process of imitating trial-and-error learning, reinforcement learning allows computers to create tactics, find solutions to complicated issues, and adjust to changing settings, so opening the way for systems that are continually becoming more intelligent.